Melatonin is one of the most important biochemicals in the human body. It helps to regulate sleep-wake cycles, keeping our internal clocks on track. It also is important in DNA repair and key cell metabolic processes. Recent studies have found that melatonin also has a neuroprotective effect, helping to prevent long-term damage from both everyday insults and more pathological disease processes. In fact, according to new research on melatonin and hemorrhagic stroke, melatonin supplements may even facilitate healing and prevent long-term damage after very serious brain injuries.
Stroke: A Leading Cause of Disability and Death
A stroke, also called a cerebrovascular accident, is a shockingly common event, affecting almost 800,000 people a year. Strokes occur when areas of the brain do not get adequate oxygen, damaging or killing cells. Because our brains are responsible for movement, thought, personality and key biological processes, this death of cells can have devastating consequences.
People who have suffered a stroke will often notice unilateral, or one-sided, paralysis. Half of their face may droop, or one of their arms suddenly become unable to move. They also can have symptoms such as the inability to speak or inability to swallow. In severe strokes, death can occur rapidly. However, the damage caused by strokes can be prevented or lessened when they are caught and treated early.
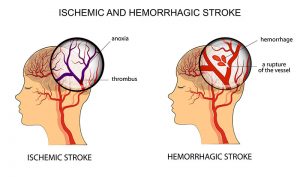 There are two common types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel supplying brain tissue is blocked. Cells that receive blood flow and oxygen from this vessel thus are starved. Hemorrhagic strokes, on the other hand, are caused by bleeding in the brain. This bleeding causes clots, preventing the flow of new blood to cells. The bleeding also can cause a lack of blood flow downstream from the blood vessel rupture. While ischemic strokes are the most common, they are easiest to treat. Medications that stop the blockage are available and extremely effective when given soon after the stroke begins. Hemorrhagic strokes, representing just 15 percent of strokes, are more deadly and much more difficult to treat.
There are two common types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel supplying brain tissue is blocked. Cells that receive blood flow and oxygen from this vessel thus are starved. Hemorrhagic strokes, on the other hand, are caused by bleeding in the brain. This bleeding causes clots, preventing the flow of new blood to cells. The bleeding also can cause a lack of blood flow downstream from the blood vessel rupture. While ischemic strokes are the most common, they are easiest to treat. Medications that stop the blockage are available and extremely effective when given soon after the stroke begins. Hemorrhagic strokes, representing just 15 percent of strokes, are more deadly and much more difficult to treat.
Melatonin’s Role in the Brain
What does melatonin have to do with hemorrhagic stroke? While melatonin is best known for its effects on the sleep-wake cycle, it also has neuroprotective effects. That is, it can protect brain cells from injury. Part of this effect is due to melatonin’s role as an antioxidant. As our bodies go through normal metabolic processes, free oxygen radicals are produced. These radicals can do a great deal of damage to cells and to DNA. Antioxidants such as melatonin bind to these free radicals so they can be removed without causing damage.
When cells are damaged, such as during a stroke, they produce even more free radicals as they attempt to deal with the harm. In turn, these free radicals cause more damage and can actually increase the harmful events of the stroke. Melatonin has been found to lessen damage in brain tissues that suffer a lack of blood flow. This hormone also acts as an anti-inflammatory, protecting brain cells from being damaged by serious brain infections. These combined effects can have an immensely positive impact on a person’s prognosis, or chances of recovery following an injury.
Melatonin and Hemorrhagic Stroke
According to new research, melatonin supplements may be an important treatment following a hemorrhagic stroke. Research has found that melatonin can reduce brain cell and neuronal death following hemorrhagic strokes. While this does not stop the stroke, it gives people a better chance of surviving the stroke and recovering most or all of their abilities afterward. In fact, hemorrhagic stroke patients who were given melatonin did not have to be intubated as long as those who did not receive it, and also had shorter ICU stays.
Identifying and Treating Strokes: It’s About Time
It appears that melatonin may be very important in protecting the brain from a variety of insults. However, a great deal more research has to be done before this is a standard treatment for hemorrhagic stroke patients. It remains crucial that strokes be identified and treated as quickly as possible. Doctors who specialize in stroke treatment recommend that everyone know the FAST mnemonic in dealing with a suspected stroke:
- Face: Look at the person’s face and ask them to make a facial expression. If half their face is drooping or appears to be unable to move, this is a suspected stroke.
- Arms: Ask the person to lift both arms. Stroke victims may be unable to lift an arm, or unable to keep it lifted.
- Speech: Can the person repeat a phrase? Are they slurring their words?
- Treatment: If any of these signs are positive, call emergency services immediately. Many strokes can be treated if caught quickly.
Melatonin appears to have many more purposes than previously realized. This hormone may soon be an important part of treatment for a variety of brain injuries. Until then, getting prompt medical care for strokes remains the best way of preventing death and disability from these devastating events.